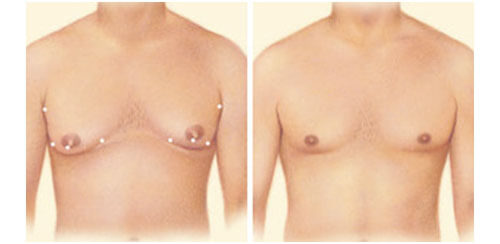
Gynecomastia
- Gynecomastia is a condition of over-developed or enlarged breasts in men that can occur at any age. The condition can be the result of hormonal changes, heredity, obesity, or the use of certain drugs.
- Gynecomastia can cause emotional discomfort and impair your self confidence. Some men may even avoid certain physical activities and intimacy simply to hide their condition.
- Gynecomastia is characterized by:
- Excess localized fat
- Excess glandular tissue development
- Sometimes excess breast skin
- Presence unilaterally (one breast) or bilaterally (both breasts)
- Gynecomastia surgery candidates include:
- Men whose condition cannot be corrected through alternative medical treatments
- Healthy individuals who do not have a life-threatening illness or medical conditions that can impair healing
- Non-smokers and non-drug users
- Men with a positive outlook and specific goals in mind for improving the physical symptoms of gynecomastia
- Men who are physically healthy and of relatively normal weight
- Men who have realistic expectations
- Men whose breast development has stabilized
- Men who are bothered by the feeling that their breasts are too large
- Adolescents may benefit from surgery, although secondary procedures may be needed in the future should breast development continue.
- During your gynecomastia surgery recoveryperiod, dressings or bandages will be applied to your incisions and an elastic bandage or support garment may be used to minimize swelling and support your new chest contour as it heals after surgery.
- A small, thin tube may be temporarily placed under the skin to drain any excess blood or fluid that may collect.
- You will be given specific instructions that may include how to care for the surgical site and drains, medications to apply or take orally to aid healing and reduce the potential for infection, specific concerns to look for at the surgical site or in your general health, and when to follow up with your plastic surgeon.
- Be sure to ask your plastic surgeon specific questions about what you can expect during your individual recovery period.
- Where will I be taken after my surgery is complete?
- What medication will I be given or prescribed after surgery?
- Will I have dressings/bandages after surgery? When will they be removed?
- Are stitches removed? When?
- When can I resume normal activity and exercise?
- When do I return for follow-up care?
- It’s very important to follow your plastic surgeon’s instructions and attend follow-up visits as scheduled.
- The final results of gynecomastia surgery are permanent in many cases. However, if gynecomastia resulted from the use of certain prescription medications, drugs (including steroids), or weight gain you must be fully free from these substances and remain at a stable weight in order to maintain your results.
- Please discuss this with your physician before making changes to your prescription medications.
- Recovering from gynecomastia surgery at home
- If you experience shortness of breath, chest pains, or unusual heart beats, seek medical attention immediately. Should any of these complications occur, you may require hospitalization and additional treatment.
- Following your physician’s instructions is essential to the success of your surgery.
- It’s important that the surgical incisions are not subjected to excessive force, swelling, abrasion, or motion during the time of healing. Your doctor will give you specific instructions on how to care for yourself.
- The decision to have plastic surgery is extremely personal, and you will have to decide if the benefits will achieve your goals and if the risks and potential complications of gynecomastia surgeryare acceptable.
- You will be asked to sign consent forms to ensure that you fully understand the procedure and any risks and potential complications.
- Gynecomastia surgery risks include:
- Reactions to tape, suture materials, glues, topical preparations or injected agents
- Anesthesia risks
- Bleeding (hematoma)
- Blood clots
- Breast asymmetry
- Breast contour and shape irregularities
- Changes in nipple or breast sensation may be temporary or permanent
- Damage to deeper structures – such as nerves, blood vessels, muscles, and lungs – can occur and may be temporary or permanent
- Deep vein thrombosis, cardiac and pulmonary complications
- Fatty tissue found in the breast might die (fat necrosis)
- Fluid accumulation (seroma)
- Infection
- Persistent pain
- Poor wound healing
- Possibility of revisional surgery
- Unfavorable scarring
- These risks and others will be fully discussed prior to your consent. It’s important that you address all your questions directly with your plastic surgeon.
